Electricity
Generating electricity, How-to!
Magnets and coils of wire
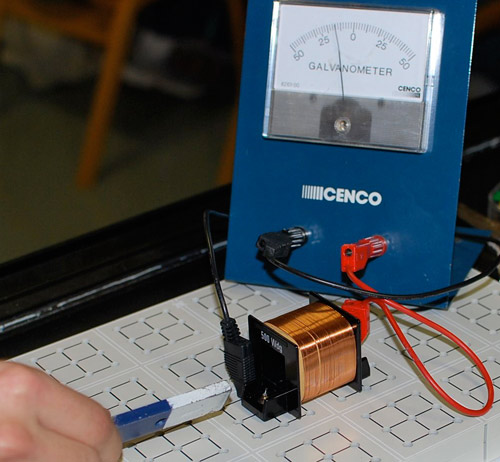 This is a simple apparatus for measuring the Faraday effect--Michael Faraday (1791-1867).
This is a simple apparatus for measuring the Faraday effect--Michael Faraday (1791-1867).
- There is a galvanometer acting as an ammeter which measures electric current in a circuit.
- The copper wire that you can see is looped around many times forming a coil.
- That copper wire coil is part of the circuit.
Make the current flow
Current is flowing when the needle on the meter is away from 0.
- Where can you place the magnet such that you generate a current?
- Or alternately, under what circumstances do you see a current flowing?
- When a wire loop is placed in the vicinity of a magnet,
- If either the magnet or the loop move,
...an electric current is created within the loop! ...for as long as the motion continues. [bicycle generator]
A/C electricity
A/C means "alternating current". Current in a circuit alternates in direction. The direction changes 60 times / second, "60 Hz". This is what you get when you plug into a wall socket.
DC means direct current. This is what you get when you attach wires to a battery. The current always flows the same way: Electrons flow from the negative pole, through the circuit to the positive pole of the battery.
Most of the electricity generated in this country is AC, and is generated by electrical turbines: Magnets on a shaft are spun around (by a turbine) close to wire coils.
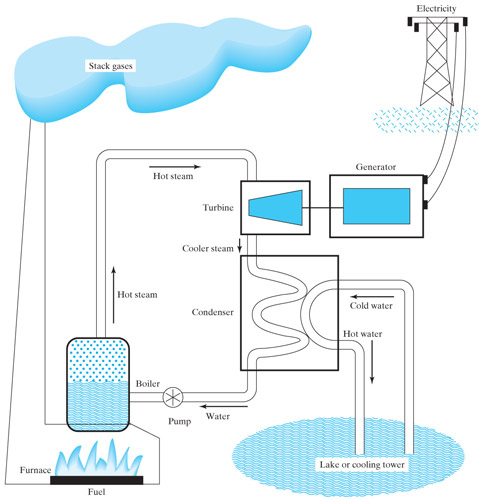
- Heat water
- It turns to steam.
- Steam occupies about 1000 times the volume of the same number of moles of water.
- The expansion of the steam through propellor-like blades makes a turbine spin.
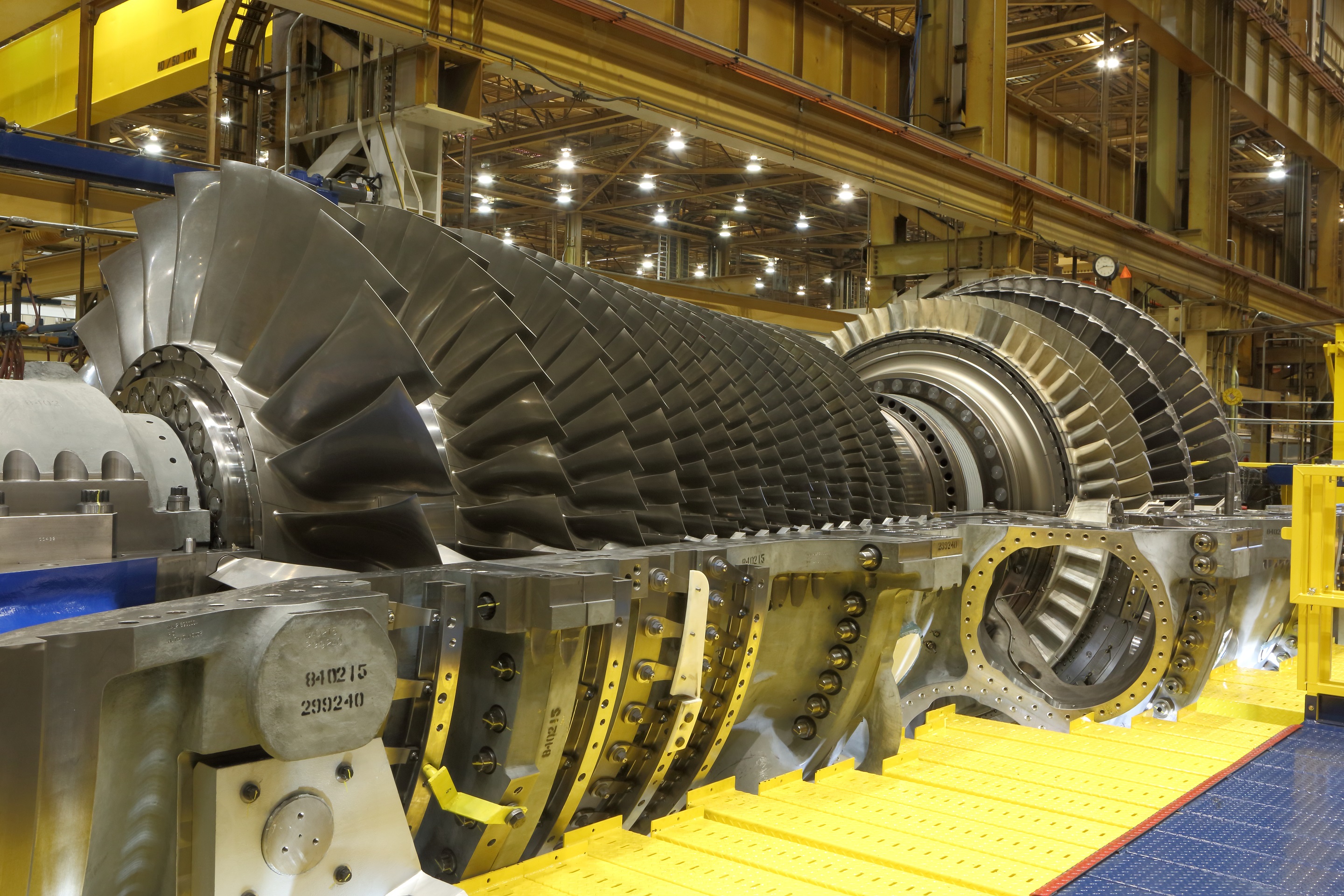

General Electric - Magnets connected to the shaft of the turbine are spun past wire coils.
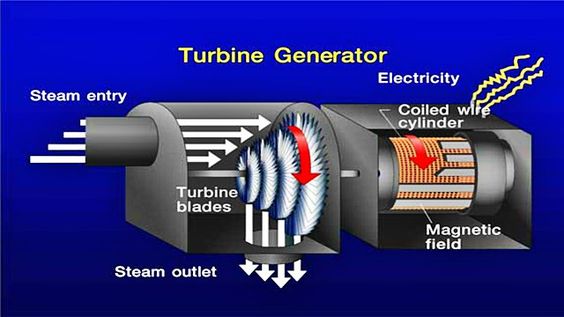
?? - ...generating AC electricity.
- Burning coal: A controlled chemical reaction (combustion) generates the heat (and ->CO${}_2$)
- Burning natural gas (->CO${}_2$)
- Burning oil (->CO${}_2$)
- Geothermal: water comes in contact with hot rocks under the earth (Renewable)
- Nuclear: A controlled nuclear reaction generates the heat (~R)
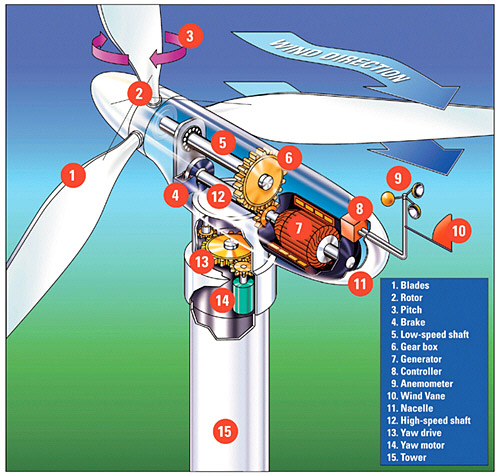 Turbines can also be turned by mechanical forces:
Turbines can also be turned by mechanical forces:
- Wind turbine: Wind turns a propeller (R)
- Hydroelectric: Falling water from behind a dam drives a turbine (R)

General Electric
 Solar photovoltaic (PV) panels have semiconductors (Silicon is a common one) that absorb sunlight and generate DC electricity.
Solar photovoltaic (PV) panels have semiconductors (Silicon is a common one) that absorb sunlight and generate DC electricity.
If you want to connect to the electric grid with your solar panels, you need to use an inverter to convert DC to AC electricity.
Many solar panels have the option of buying them with a microinverter installed on the panel itself.

1000 MW electric generators
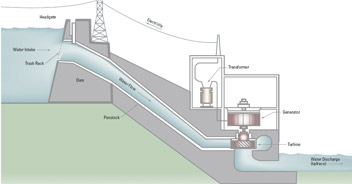 |
Gravitational Energy 60,000 tonnes of water / second |
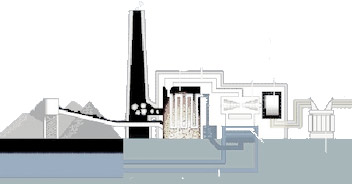 |
Chemical Energy 10,000 tonnes of coal / day |
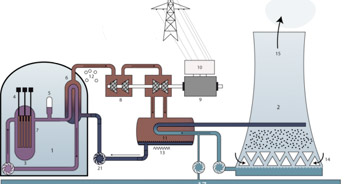 |
Nuclear Energy 100 tonnes of uranium / year |
Which would you guess is most dangerous?
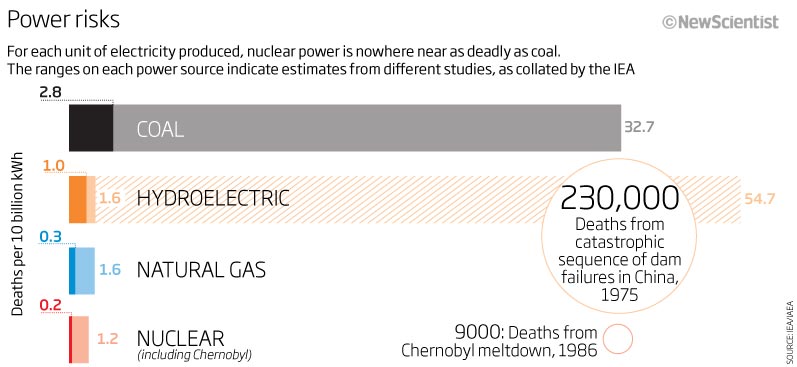
Source: New Scientist (2011)
Since the 2011 study above, a Harvard, School of Public Health study (2021) found that pollution from fossil fuels (primarily coal and diesel) may be responsible for as many as 1 in 5 deaths worldwide.
Here's an excellent overview of costs / land use / comparisons (2016) (energy.gov).
Image credits
Alternative energy news, M-power (UK), U.S. EIA, Denis Egan, Solar Power Rocks