[13.4] - Green's theorem problems
- Let $C$ be the triangle path $(0,0)\to(1,1)\to(0,1)\to(0,0)$.
The orientation of the path is negative. The vector integral around the outside is equal to the positive orientation: $$\begineq \oint_{-C}(-2y\,dx+3x\,dy)&=&\\ \oint P\,dx+Q\,dy &=&\iint\left(\frac{\del Q}{\del x}-\frac{\del P}{\del y}\right)\,dA\\ &=&\iint\left(3-(-2)\right)=5\iint dA=5*\frac 12. \endeq$$
-
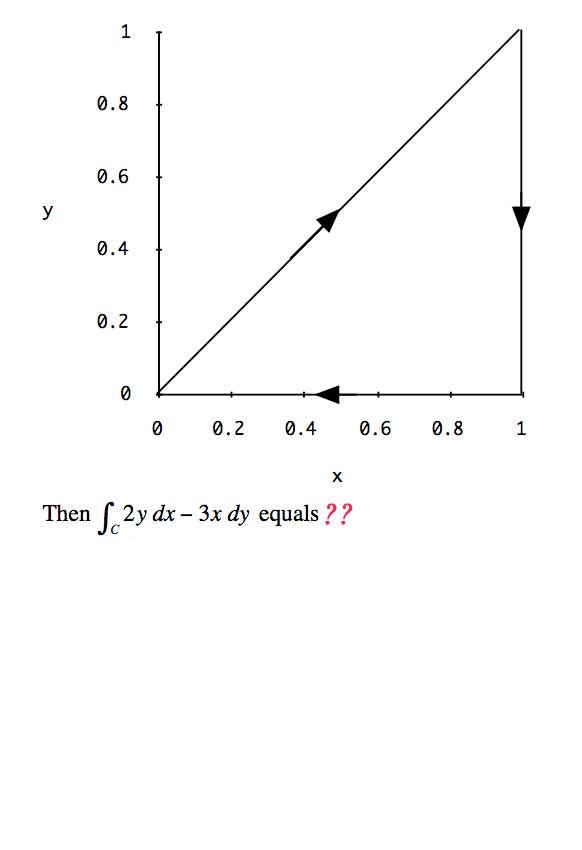
Use Green's Theorem to calculate $\oint_C(y-x)\,dx
+(2x-y)\,dy$ where $C$ is the boundary of the rectangle shown.

$$Q_x-P_y=2-1=1$$ so $$\oint_C P\,dx+Q\,dy=\int_{-4}^{4}\int_{-3}^3 (1) \,dx\,dy=8\times 6=48.$$
-
Compute $\oint_C\left(-\frac{xy^4}{2}\right)\,dx +
\left(x^2y^3\right)\,dy$ where $C$ is the curve shown below.

$$Q_x-P_y=2xy^3-(-4xy^3/2)=4xy^3$$ then $$\oint_C...=\int_{x=-1}^1\int_{y=-\sqrt{1-x^2}}^1 4xy^3\,dy\,dx =...=0$$
-
Use Green's Theorem to evaluate the following line integrals:
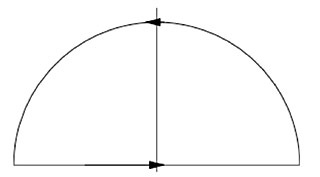
- $\oint_C\left(\arctan(x^2)-y^2\right)\,dx+
\left(x^2y-\ln(y^2+1)\right)\,dy$ where $C$ is the semicircle $y=\sqrt{4-x^2}$ together with the line segment $(-2,0)\to(2,0)$ as shown.
-
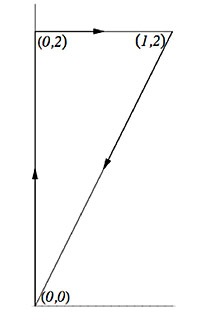
$\oint_C xy\,dx+(x^2+y^2)\,dy$ where $C$ is this triangle.
- $\oint_C\left(\arctan(x^2)-y^2\right)\,dx+
\left(x^2y-\ln(y^2+1)\right)\,dy$ where $C$ is the semicircle $y=\sqrt{4-x^2}$ together with the line segment $(-2,0)\to(2,0)$ as shown.
-
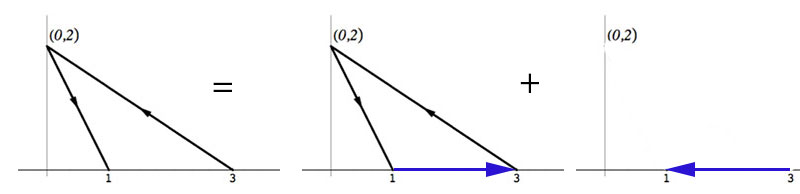
Consider the non-closed curve $C$, $(3,0)\to(0,2)\to (1,0)$ as shown. Figure out a way to use Green's Theorem to help you compute
$\int_C(x+y)\,dx+(3x-y)\,dy$.

Hint: