Acid Rain - a success story
In the U.S. we had a serious problem with "Acid Rain" in the 1980s. Now we don't. Why?
Preparation assignment
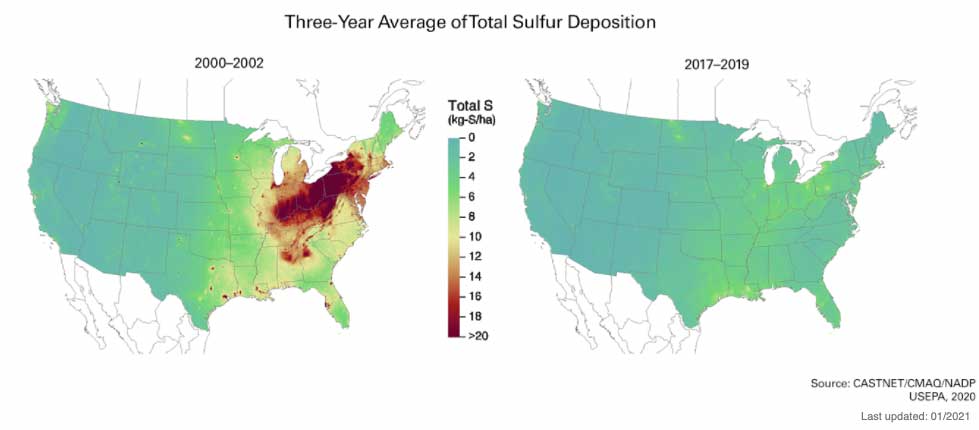
Acid Rain - According to the map above acid rain was a bigger problem in the eastern US than in the west. As you read, try to formulate some guesses about why that is.
Using the EPA's site on acid rain, and / or other useful sites that you find, look for answers to these background questions about acid rain.
- What are the pollutants that cause acid rain?
Sulfur dioxide ($SO_2$) and nitrogen oxides($NO_x$)
- What are the major sources of those pollutants?
Burning of fossil fuels, vehicles and heavy equipment, manufacturing, oil refineries.
Two thirds of SO2 and one fourth of NOX in the atmosphere come from electric power generators.
- What are the environmental effects of acid rain?
Acidic rain causes aluminum to come out of the soil.
...and High levels of Al in ponds are hazardous to fish + animals.
Acid rain also removes minerals and nurients from the soil that are essential for [plant] growth.
- How are the effects of acid rain measured? You should discuss what "pH" is, and what values are normal or problematic.
Acid rain is measured by the pH scale which determines if a substance is acidic, neutral, or alkaline. [...] Acids have a pH reading of less than 7 and alkalines have a pH reading of more than 7
Acids include $H_2SO_4$ (sulfuric acid), $HN0_3$ (nitric acid), $H_2CO_3$ (carbonic acid).
Bases include $NaOH$ (sodium hydroxide).
- Look up the pH of...
- Human blood
- saliva
- urine
- stomach acid
Normal rain has a pH of about 5.6, which is slightly acidic because carbon dioxide dissolves into it forming a weak acid. Acid rain typically has a pH between 4.3 and 4.4.
If the ph is lower than 4, it causes fish's eggs not to hatch and die because the fish cannot handle the acidity
Some of you cited hazards to fish at pH 5 and below.