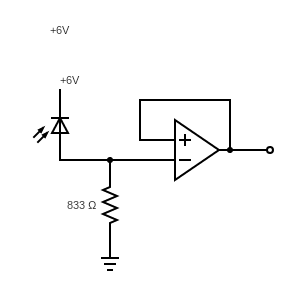
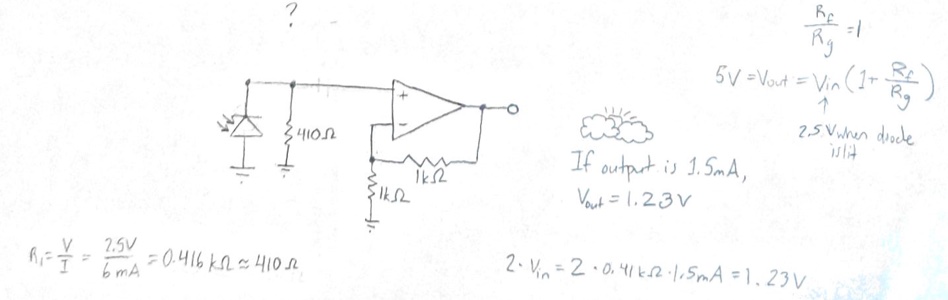
Worksheet 4 - Op Amps
Here is WS4 (pdf).
Output impedance: The output impedance of an ideal op-amp itself approaches zero. That is, it will do quite a bit to keep its two inputs at the same voltage, in spite of whatever load is put on its output.
Input impedance: Set the input voltage to some value, say $V_\text{in}=$5V. If you can calculate the current flow into the circuit, $I_\text{in}$, as a result of following our "two rules" for op amps, then the input impedance of the circuit is: $$Z\text{in}=\frac{V_\text{in}}{I_\text{in}}.$$